Every device connected to the internet has an IP address. But behind that simple number lies a decades-long evolution in how addresses are allocated, organized, and routed — an evolution that fundamentally changed the scale and efficiency of the modern internet. Classful addressing, introduced in 1981, divided the entire IPv4 address space into five rigid classes that worked well when the internet had only thousands of connected devices. By the early 1990s it was clear those fixed boundaries were accelerating IPv4 exhaustion at catastrophic speed — a company needing 300 addresses was forced into a Class B block of 65,534, wasting 99% of the allocation. The 1993 introduction of Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) replaced that rigid system with variable-length subnet masking, allowing networks to be sized precisely to actual requirements. Today, every network on the internet runs on classless addressing principles. Whether you are a student pursuing CCNA or Network+ certification, a network administrator designing enterprise infrastructure, or a developer building cloud-native applications, understanding the difference between classful and classless addressing is foundational knowledge that underpins everything from subnet design to BGP routing and cloud VPC configuration.
IP Addressing Landscape in 2026
The IPv4 address space contains exactly 4,294,967,296 addresses — a number that seemed virtually unlimited when the internet had thousands of connected devices in 1981. The classful addressing system that managed those early addresses divided them into fixed blocks sized for large organizations, medium businesses, and small networks, with no middle ground. That rigidity proved catastrophic as internet adoption accelerated. IPv4 addresses were fully exhausted at the regional level on April 21, 2017. The classless CIDR system introduced in 1993 extended the usable life of IPv4 by decades through efficient allocation — and today forms the absolute foundation of all IP networking from home routers to global BGP routing tables.
Classful Addressing: The Fixed-Class Model
Definition
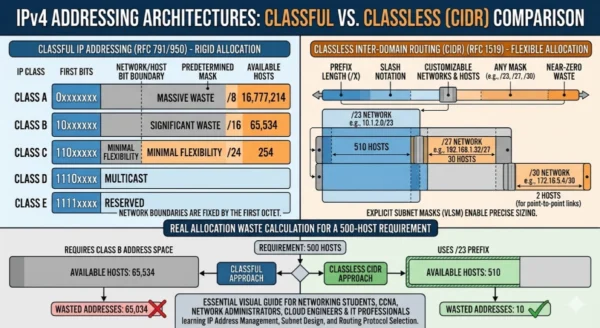
Classful addressing is the original IPv4 address allocation architecture introduced in 1981, which divides the 32-bit IP address space into five predefined classes based on the leading bits of each address. The class of an IP address is determined automatically from the address itself — no subnet mask information needs to be communicated because the class implies a fixed, predetermined subnet mask. Class A uses the first octet for the network portion, Class B uses the first two octets, and Class C uses the first three octets. This implicit masking made early routing simple but created enormous inflexibility. Organizations received exactly one of three sizes — 16.7 million addresses, 65,534 addresses, or 254 addresses — with no option for anything in between, making efficient allocation structurally impossible at internet scale.
Advantages
- Conceptual simplicity: Class is determined directly from the IP address with no additional subnet mask information needed — ideal for learning networking fundamentals
- Implicit masking: Routers using classful protocols automatically know the subnet mask from the address, reducing routing update size in early implementations
- Clear boundaries: Predefined address ranges make class identification instant — any address starting with 192 is immediately recognizable as Class C
- Simple implementation: Early network devices required minimal processing — no VLSM calculations, no prefix length parsing, no variable-length considerations
- Educational value: Class-based structure remains the foundation for understanding IP address organization, private ranges, and networking certification curricula
- Legacy compatibility: Organizations with pre-1993 infrastructure understand classful boundaries that still influence private address range selection today
Disadvantages
- Massive address waste: A company needing 300 addresses must accept a Class B block of 65,534, wasting over 99% of the allocation permanently
- No middle ground: Only three practical sizes — 16.7 million, 65,534, or 254 usable hosts — with nothing between Class C and Class B for common mid-size needs
- Routing table explosion: Without route aggregation, each classful network requires a separate routing table entry, creating unsustainable table growth
- Accelerated IPv4 exhaustion: Structural over-allocation was the primary driver of IPv4 address exhaustion, reaching regional depletion by 2011
- No VLSM support: Cannot subdivide networks into variable-size subnets — all subnets within a classful network must use the same fixed mask
- Obsolete protocols: RIPv1 and IGRP supporting classful routing are deprecated — no modern network should operate classful routing protocols
IP Address Classes Breakdown:
Class A (0.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255): First bit always 0. /8 implied mask. 126 networks, 16,777,214 hosts each. Designed for massive organizations. Class B (128.0.0.0 – 191.255.255.255): First two bits 10. /16 implied mask. 16,384 networks, 65,534 hosts each. Furthermore, Class C (192.0.0.0 – 223.255.255.255): First three bits 110. /24 implied mask. 2,097,152 networks, 254 hosts each. Additionally, Class D (224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255): Reserved for multicast — routing protocols like OSPF and RIP use this range. Moreover, Class E (240.0.0.0 – 255.255.255.255): Reserved for experimental use — never deployed publicly on the internet.
Classless Addressing: The CIDR Revolution
Definition
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR), introduced by the IETF in 1993 through RFC 1518 and RFC 1519, replaced classful addressing by eliminating the concept of fixed address classes entirely. Instead of the address implying a fixed mask, CIDR uses explicit prefix notation — the slash notation (e.g., 192.168.1.0/24) — where the number after the slash specifies exactly how many bits form the network portion of the address. This variable-length subnet masking allows networks to be sized to any power of two from /1 to /32, letting allocators assign precisely the number of addresses an organization needs. A company needing 500 addresses receives a /23 block of 512 addresses rather than a Class B block of 65,534 — saving 65,022 addresses that can be allocated to other organizations. CIDR also enables route aggregation (supernetting), where multiple contiguous networks can be announced as a single routing entry, dramatically reducing global BGP routing table size and improving internet routing efficiency.
Advantages
- Precise allocation: Networks sized to exactly what is needed — /27 for 30 hosts, /23 for 500 hosts, /20 for 4,094 hosts — eliminating structural waste
- Route aggregation: Multiple contiguous subnets summarized into single routing entries, reducing BGP table size and improving global routing performance
- VLSM support: Variable-Length Subnet Masking allows different subnet sizes within the same network block for hierarchical, efficient network design
- IPv4 life extension: Efficient allocation significantly slowed IPv4 exhaustion, extending the usable life of the 32-bit address space by decades
- Modern protocol support: All current routing protocols — RIPv2, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP — carry explicit prefix lengths enabling full classless operation
- Cloud and VPC compatibility: AWS VPCs, Azure VNets, and GCP networks all use CIDR notation natively for subnet definition and routing configuration
- Supernetting: Contiguous address blocks can be aggregated into larger supernets, enabling hierarchical routing and scalable internet architecture
Disadvantages
- Steeper learning curve: VLSM calculations require understanding binary arithmetic, prefix lengths, and subnet boundaries that classful addressing made implicit
- Planning complexity: Efficient CIDR deployment requires careful IP address management planning to avoid fragmentation and exhaustion of allocated blocks
- Routing table explosion risk: Poorly aggregated CIDR announcements can grow routing tables — proper summarization discipline is essential at scale
- Explicit mask requirement: Every routing update must carry the subnet mask explicitly — classful protocols like RIPv1 cannot participate in classless environments
- Miscalculation risk: Incorrect subnet mask calculations can cause address overlap, connectivity failures, and security boundary violations
- IPAM requirement: Large CIDR deployments require IP Address Management tools to track allocations, prevent conflicts, and plan hierarchical address space efficiently
CIDR Notation and Block Sizing Reference:
/30 (4 addresses, 2 usable): Point-to-point links between routers. /27 (32 addresses, 30 usable): Small department or branch office network. Furthermore, /24 (256 addresses, 254 usable): Standard small network — equivalent to legacy Class C. Additionally, /23 (512 addresses, 510 usable): Medium network replacing two /24 blocks. Moreover, /22 (1,024 addresses, 1,022 usable): Large department or small campus network. /16 (65,536 addresses, 65,534 usable): Enterprise campus — equivalent to legacy Class B. /8 (16,777,216 addresses): Large ISP or cloud provider block — equivalent to legacy Class A.
Technical Architecture Deep Dive
Classful Addressing Architecture
- Class determined from leading bits of first octet — no additional mask information needed
- Fixed subnet masks: Class A /8, Class B /16, Class C /24 — no variation possible
- Routing updates carry only the IP address — subnet mask implied by class
- Classful routing protocols (RIPv1, IGRP) perform automatic summarization at class boundaries
- Discontiguous subnets cause routing problems due to automatic summarization behavior
- Subnetting within a class must use uniform masks — VLSM not supported
- Network boundary determined entirely by address class, not administrative choice
Classless CIDR Architecture
- Prefix length explicitly specified using slash notation — no class inference required
- Any prefix length from /1 to /32 valid — network sized precisely to requirements
- Routing updates carry both IP prefix and subnet mask — classless protocols required
- Route aggregation combines multiple contiguous prefixes into single routing entry
- VLSM allows different subnet sizes within same allocated block for hierarchical design
- CIDR blocks follow three rules: contiguous addresses, power-of-two block size, first address divisible by block size
- Supernetting aggregates smaller networks into larger blocks for routing efficiency
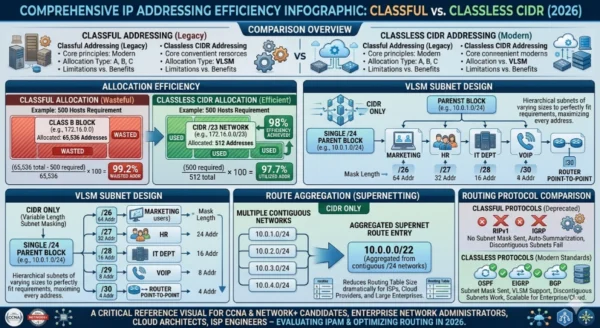
Address Allocation Efficiency: Real-World Comparison
Classful Allocation — 500 Host Requirement
- Organization requires 500 IP addresses for a medium-sized network
- Class C maximum is 254 usable hosts — insufficient for requirement
- Next available class is Class B with 65,534 usable host addresses
- Organization receives full Class B block: e.g., 172.16.0.0/16
- 500 addresses used, 65,034 permanently wasted in the allocation
- 99.2% of the allocated address block serves no purpose
- Wasted addresses unavailable to other organizations globally
Classless CIDR Allocation — 500 Host Requirement
- Organization requires 500 IP addresses for the same network
- CIDR calculation: next power of two above 500 is 512 (/23 block)
- Organization receives 192.168.0.0/23 — exactly 512 addresses, 510 usable
- Only 10 addresses unused — 98% allocation efficiency
- 65,022 addresses saved compared to classful allocation
- Saved addresses available for allocation to other organizations
- Network sized precisely to requirement with room for minimal growth
Routing Protocol Support Comparison
| Routing Protocol | Type | Subnet Mask in Updates | VLSM Support | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIPv1 | Classful | No — mask implied by class | No | Deprecated |
| IGRP | Classful | No — mask implied by class | No | Deprecated |
| RIPv2 | Classless | Yes — explicit in updates | Yes | Legacy use |
| OSPF | Classless | Yes — explicit in LSAs | Yes | Modern standard |
| EIGRP | Classless | Yes — explicit in updates | Yes | Modern standard |
| BGP | Classless | Yes — NLRI carries prefix length | Yes | Internet backbone |
Use Cases and Real-World Applications
Where Classful Addressing Still Matters
- Certification study: CCNA, Network+, CCIE, and Security+ exams all test classful address recognition, class boundaries, and private range identification
- Legacy system maintenance: Organizations running pre-1993 infrastructure or classful routing protocols require classful knowledge for accurate troubleshooting
- Private address ranges: RFC 1918 private ranges (10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, 192.168.0.0/16) still align with original class boundaries — recognizing them requires class awareness
- Historical documentation: Network diagrams and runbooks from the 1980s-early 1990s use classful notation — reading legacy documentation requires understanding the class system
- Conceptual foundation: Understanding classful limitations explains why CIDR was designed the way it was — essential context for deep networking expertise
Where Classless CIDR is Essential
- Enterprise network design: VLSM enables efficient hierarchical addressing with different subnet sizes per department, floor, or function within a single allocated block
- ISP address management: Internet Service Providers allocate customer blocks precisely to requirements using CIDR, maximizing utilization of their Regional Internet Registry allocations
- Cloud VPC configuration: AWS VPCs, Azure Virtual Networks, and GCP VPCs are defined entirely using CIDR notation for address space, subnet creation, and routing rules
- Internet routing: All BGP route announcements on the internet use CIDR prefixes — the entire global routing table of 900,000+ prefixes is organized on classless principles
- Data center networking: Server farm subnetting, management network isolation, and storage network segmentation all require VLSM precision that classful addressing cannot provide
Industry Deployment Patterns
| Domain | Classful Relevance | Classless CIDR Application |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Platforms | None — AWS, Azure, GCP use CIDR exclusively for all VPC and subnet configuration | VPC CIDR blocks, subnet carving, security group IP ranges, VPN tunnel definitions |
| Enterprise Networks | Legacy documentation reference only — no new enterprise design uses classful addressing | VLSM hierarchical design, departmental subnetting, route summarization at WAN boundaries |
| Internet Service Providers | Historical RIR allocation records reference original class assignments | Customer prefix allocation, BGP route announcements, prefix filtering and aggregation |
| Data Centers | Private range recognition (10.x.x.x, 172.16.x.x, 192.168.x.x) for management | Server farm subnets, storage networks, out-of-band management, overlay network addressing |
| Education | Core curriculum for all networking certifications and university CS networking courses | Subnetting labs, OSPF configuration, BGP policy simulation, cloud networking exercises |
12 Critical Differences: Classful vs Classless Addressing
Aspect | Classful Addressing | Classless Addressing (CIDR) |
|---|---|---|
| Address Structure | Five fixed classes (A, B, C, D, E) with predetermined network and host bit boundaries | No fixed classes — prefix length explicitly defined using slash notation for any boundary |
| Subnet Mask | Implied by address class — /8 for Class A, /16 for Class B, /24 for Class C — no choice | Variable-length subnet mask (VLSM) — any prefix from /1 to /32 valid and explicitly stated |
| Address Efficiency | Severe waste — organization needing 500 hosts receives 65,534 (Class B) wasting 99% | Precise allocation — organization needing 500 hosts receives /23 block of 512 wasting under 2% |
| Routing Updates | Subnet mask not included — classful protocols infer mask from address class automatically | Subnet mask carried explicitly in every routing update by all classless protocols |
| Route Aggregation | No route summarization across class boundaries — each network requires individual entry | CIDR supernetting aggregates multiple contiguous prefixes into single routing table entry |
| Routing Protocols | RIPv1 and IGRP — both deprecated and no longer used in modern network deployments | RIPv2, OSPF, EIGRP, and BGP — all current industry-standard protocols are classless |
| VLSM Support | Not supported — all subnets within a classful network must use identical subnet masks | Full VLSM support — different subnet sizes freely mixed within the same allocated block |
| Network Boundaries | Rigid class boundaries fixed by address leading bits — cannot be administratively modified | Flexible boundaries defined by prefix length — adjusted to match actual network requirements |
| Supernetting | Not possible — cannot aggregate below class boundary for route summarization | Fully supported — multiple networks combined into single supernet announcement |
| IPv4 Conservation | Primary cause of IPv4 exhaustion through structural over-allocation and wasted blocks | Extended IPv4 usability by decades through precise allocation and efficient reuse |
| Cloud Compatibility | Not compatible — AWS, Azure, and GCP VPCs require CIDR notation exclusively | Native cloud support — all major cloud platforms use CIDR for VPC and subnet configuration |
| Modern Relevance | Obsolete for network design — relevant only for certification study and legacy troubleshooting | Universal standard — every network built after 1993 operates on classless CIDR principles |
Implementation and Subnet Design Guide
CIDR Subnet Design Process
- Requirements Gathering: First, document the number of hosts required per subnet including 20-30% growth buffer, identifying each network segment — servers, clients, management, DMZ, and inter-router links separately.
- Block Size Calculation: Then, for each segment, identify the smallest power of two that exceeds host requirements plus two (network and broadcast addresses). For 50 hosts: 2^6 = 64 addresses — use /26.
- Address Space Planning: Additionally, select a parent CIDR block large enough to contain all subnets with room for future expansion. Allocate larger subnets first to avoid fragmentation within the address space.
- VLSM Allocation: Furthermore, carve subnets from the parent block using VLSM — assign the largest subnets first, then progressively smaller ones, ensuring non-overlapping boundaries.
- Route Summarization Planning: Subsequently, design subnet allocations so that department or site address ranges can be summarized into single routing entries at aggregation points.
- Documentation and IPAM: Finally, record all allocations in an IP Address Management system, including subnet purpose, assigned devices, responsible team, and planned expansion capacity.
CIDR Subnetting: Worked Example
Designing subnets for a company with four departments using VLSM from a 192.168.1.0/24 allocation:
Parent Block: 192.168.1.0/24 (256 addresses total)
Department Requirements:
Engineering: 60 hosts needed → /26 (64 addresses, 62 usable)
Marketing: 28 hosts needed → /27 (32 addresses, 30 usable)
Finance: 12 hosts needed → /28 (16 addresses, 14 usable)
Management: 6 hosts needed → /29 (8 addresses, 6 usable)
Router Links: 2 hosts needed → /30 (4 addresses, 2 usable) ×2
VLSM Allocation (largest first):
192.168.1.0/26 → Engineering (62 usable: .1 – .62)
192.168.1.64/27 → Marketing (30 usable: .65 – .94)
192.168.1.96/28 → Finance (14 usable: .97 – .110)
192.168.1.112/29 → Management ( 6 usable: .113 – .118)
192.168.1.120/30 → Router Link 1 ( 2 usable: .121 – .122)
192.168.1.124/30 → Router Link 2 ( 2 usable: .125 – .126)
Addresses used: 128 of 256 (50% efficiency)
Remaining free: 192.168.1.128/25 available for future growth
Classful equivalent would require:
4 × Class C blocks = 4 × 254 usable = 1,016 addresses allocated
Only 108 needed = 89% waste
4 separate routing entries vs 1 summary route with CIDR
Migration Strategy: Classful to Classless
Phase 1: Assessment (Weeks 1-3)
- Audit all existing network addressing and document current classful assignments
- Identify all devices running classful routing protocols (RIPv1, IGRP)
- Map existing subnets and determine actual host counts per segment
- Identify discontiguous subnets that classful summarization affects
- Select IPAM tool for tracking classless allocation during and after migration
Phase 2: Design (Weeks 4-6)
- Design new CIDR address plan with VLSM-optimized subnet sizes per segment
- Plan route summarization boundaries for efficient routing table management
- Select classless replacement protocols: OSPF or EIGRP for internal, BGP for external
- Configure new addressing in lab environment and validate routing behavior
- Plan parallel operation period to minimize migration risk and downtime
Phase 3: Migration (Weeks 7-12)
- Deploy classless routing protocol on all devices while maintaining classful configuration
- Migrate subnets incrementally starting with non-critical network segments
- Validate connectivity and routing convergence after each subnet migration
- Decommission classful protocols after all segments confirmed working on CIDR
- Document final CIDR addressing in IPAM system and update network diagrams
Implementation Best Practices
Success Factors
- Always plan address space hierarchically — allocate regional blocks, then site blocks, then subnet blocks
- Reserve 25-30% of each allocated block for growth before planning subnets
- Use route summarization at every aggregation point to keep routing tables efficient
- Deploy IPAM tools from day one — manual spreadsheet tracking breaks down at enterprise scale
- Align subnet boundaries to powers of two — improves summarization and simplifies troubleshooting
- Document every subnet’s purpose, owner, and expansion capacity in IPAM before deployment
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Never allocate subnets without verifying non-overlapping boundaries — overlaps cause silent routing failures
- Avoid using classful routing protocols (RIPv1, IGRP) in any new network design — they are deprecated
- Do not allocate all available address space upfront — always reserve room for growth and future subnets
- Never mix classless and classful routing protocols on the same network segment without careful planning
- Avoid creating overly large subnets that exceed actual requirements — defeats the purpose of CIDR efficiency
- Do not skip route summarization at WAN boundaries — unsummarized prefixes bloat routing tables unnecessarily
Efficiency, Complexity and Migration Analysis
Address Efficiency
Classful: 1-99% waste depending on class fit
CIDR: Under 50% waste in worst case with optimal sizing
Learning Curve
Classful: Minutes — class recognized from address
CIDR/VLSM: Hours to days for binary subnetting mastery
Routing Table Size
Classful: One entry per class network — grows rapidly
CIDR: Aggregated supernets — dramatically reduced table size
Address Allocation Efficiency Comparison
| Host Requirement | Classful Allocation | Addresses Wasted | CIDR Allocation | Addresses Wasted | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 hosts | Class C /24 (254 usable) | 252 (99.2%) | /30 (2 usable) | 0 (0%) | 252 addresses saved |
| 30 hosts | Class C /24 (254 usable) | 224 (88.2%) | /27 (30 usable) | 0 (0%) | 224 addresses saved |
| 500 hosts | Class B /16 (65,534 usable) | 65,034 (99.2%) | /23 (510 usable) | 10 (2%) | 65,024 addresses saved |
| 1,000 hosts | Class B /16 (65,534 usable) | 64,534 (98.5%) | /22 (1,022 usable) | 22 (2.2%) | 64,512 addresses saved |
| 25,000 hosts | Class B /16 (65,534 usable) | 40,534 (61.8%) | /17 (32,766 usable) | 7,766 (23.6%) | 32,768 addresses saved |
The efficiency gains from CIDR are most dramatic for organizations needing address counts that fall between classful boundaries — particularly the gap between 254 (Class C) and 65,534 (Class B). Any organization needing between 255 and 65,533 hosts was forced into a Class B under classful addressing, regardless of actual requirement. CIDR eliminates this entirely, allowing exact power-of-two sizing. This single efficiency improvement — multiplied across millions of organizational allocations globally — is what extended the usable life of IPv4 addressing by decades beyond what classful allocation would have allowed.
Strategic Decision Framework
There Is No Genuine Choice — But Context Matters
Unlike technology decisions such as Kubernetes versus Docker Swarm or AIOps versus Traditional IT Operations where both options remain viable depending on context, classful addressing is not a genuine design choice for any new network in 2026. Classless CIDR is the universal standard. The decision framework here is about understanding when classful knowledge matters for your role — certification preparation, legacy troubleshooting, or cloud networking — and how to deploy CIDR effectively rather than choosing between the two systems.
Context-Based Knowledge Framework
| Your Context | Classful Knowledge Needed? | CIDR Knowledge Needed? | Priority Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Networking student / CCNA | Yes — class identification, private ranges, class boundaries are exam topics | Yes — VLSM subnetting, CIDR notation, route summarization are core exam skills | Master both — classful for context, CIDR for practical skills |
| Network administrator | Minimal — recognize private ranges and understand legacy documentation | Essential — all daily work involves CIDR subnet design, OSPF, and IPAM | CIDR mastery with VLSM proficiency is critical job skill |
| Cloud / DevOps engineer | Minimal — RFC 1918 private range recognition is sufficient | Essential — VPC CIDR blocks, subnet configuration, security groups use CIDR exclusively | CIDR notation fluency required for all cloud networking tasks |
| Security engineer | Basic — private range awareness for firewall rule interpretation | Essential — ACLs, firewall rules, and network segmentation all use CIDR prefix notation | CIDR required for all security policy and segmentation work |
| Legacy system maintainer | Important — troubleshooting classful networks requires understanding their behavior | Important — migrate legacy to CIDR where possible, understand coexistence limitations | Both needed — plan migration path while maintaining existing classful infrastructure |
CIDR Design Approaches for Different Network Scales
Small Network CIDR Design
For small businesses and home labs with straightforward requirements:
- Use 192.168.0.0/16 private space as parent — carve /24 subnets per function
- Apply /24 for LAN segments, /30 for router-to-router links, /28 for server clusters
- Document all assignments in a simple spreadsheet or free IPAM tool
- Plan for IPv6 dual-stack from the start even if not immediately deployed
- Use a single OSPF area or static routes — BGP not required at this scale
Enterprise CIDR Design
For large organizations requiring hierarchical, scalable addressing:
- Allocate RFC 1918 space hierarchically: /8 or /10 parent, /16 per region, /24 per site
- Design summarization boundaries so each site advertises a single summary prefix
- Use enterprise IPAM platform (Infoblox, SolarWinds, phpIPAM) from day one
- Reserve 30-40% of each block for unplanned growth before allocating subnets
- Deploy OSPF or EIGRP internally with BGP for inter-site and internet connectivity
Frequently Asked Questions: Classful vs Classless Addressing
Understanding IP Addressing for Modern Networking in 2026
The evolution from classful to classless addressing represents one of the most consequential architectural decisions in internet history — a necessary reinvention that saved the IPv4 address space from premature exhaustion and enabled the internet to scale to billions of devices. Understanding both systems gives network professionals the complete picture: classful addressing explains why private ranges look the way they do and forms the foundation of certification curricula, while classless CIDR is the universal standard that powers every network, cloud platform, and BGP routing table operating today.
Classful Addressing — Key Takeaways:
- Introduced in 1981 — obsolete for new network design since 1993
- Five fixed classes with implied masks — simple but inflexible
- Structural waste of 99%+ common for mid-size network requirements
- RIPv1 and IGRP are its routing protocols — both deprecated
- Still relevant for certification study and legacy documentation
- Private RFC 1918 ranges align with original class boundaries
Classless CIDR — Key Takeaways:
- Introduced in 1993 — universal standard for all modern networking
- Variable prefix length via slash notation — precise sizing for any requirement
- VLSM enables hierarchical, efficient enterprise network design
- Route aggregation reduces global BGP routing table size significantly
- Required by all modern protocols: OSPF, EIGRP, BGP, RIPv2
- Foundation of all cloud networking: AWS VPC, Azure VNet, GCP VPC
Practical Recommendation for 2026:
Learn classful addressing to pass your certification exams, understand private address ranges, and troubleshoot legacy systems — but never design a new network using classful principles. Every new network, subnet, cloud VPC, and firewall rule you configure should use CIDR notation with VLSM sizing. Master binary subnetting until CIDR calculations are instinctive, invest in a proper IPAM tool before your address space grows complex, and always design with route summarization in mind. The networking professionals who understand both the historical limitations of classful addressing and the precise power of CIDR are the ones who build networks that scale cleanly, route efficiently, and remain maintainable years into the future.
Whether you are studying for your first networking certification, designing your first enterprise network, or migrating legacy infrastructure to modern standards, the classful versus classless distinction is foundational knowledge that shapes how you think about every IP address allocation decision throughout your networking career. CIDR is not just the current standard — it is the lens through which all modern IP networking is understood, designed, and operated.
Related Topics Worth Exploring
IPv4 vs IPv6: Complete Guide
Explore the transition from 32-bit IPv4 addressing to 128-bit IPv6, including dual-stack deployment, address notation differences, and why IPv6 adoption continues accelerating globally in 2026.
Subnetting and VLSM Deep Dive
Master binary subnetting, VLSM design patterns, and CIDR block calculations with step-by-step examples covering every prefix length from /8 to /30 for real network design scenarios.
Logical vs Physical Memory Addresses
Understand how operating systems use address abstraction layers for memory management — a parallel concept to IP address abstraction that reinforces deep understanding of addressing across computing domains.