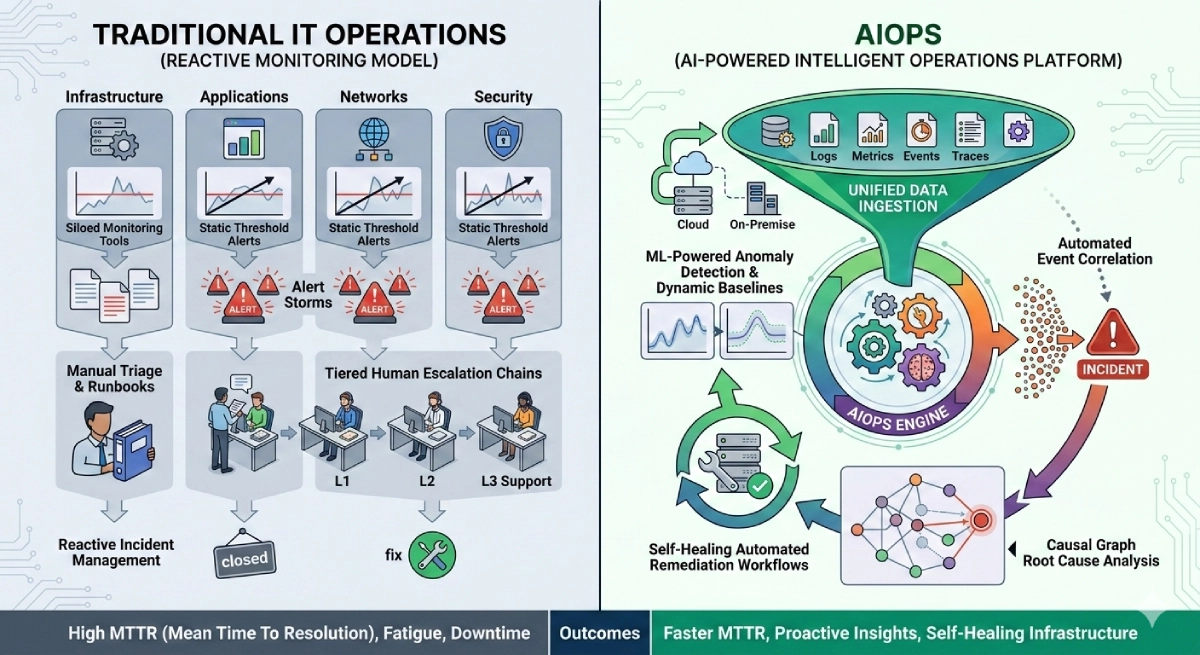
STP vs UTP: Understanding the Battle of Network Cables
In the world of networking, choosing the right cable can make a significant difference in the performance and reliability of your network. Two common options that often cause confusion are Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) and Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cables. In this article, we will delve into the differences, advantages, and best use cases of STP vs UTP cables.
What is STP Cable?
STP cable, also known as Shielded Twisted Pair cable, is designed with an extra layer of shielding to protect the transmission from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). This shielding typically consists of a metal foil or braided copper shield around each twisted pair of wires.
Advantages of STP Cable
Enhanced Protection: The shielding in STP cables offers superior protection against external electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for environments with high levels of interference or electrical noise.
Higher Bandwidth: STP cables can support higher bandwidths and data transfer rates, making them suitable for applications that require faster and more reliable connections.
Longer Cable Runs: Due to their shielding, STP cables can maintain signal integrity over longer distances without significant signal degradation.
What is UTP Cable?
UTP cable, short for Unshielded Twisted Pair cable, is the most commonly used type of Ethernet cable. It consists of pairs of twisted copper wires that are not surrounded by any additional shielding.
Advantages of UTP Cable
Cost-Effective: UTP cables are generally more affordable than STP cables, making them a popular choice for both residential and small business networks.
Flexibility: The lack of shielding makes UTP cables more flexible and easier to install compared to STP cables.
Versatility: UTP cables are suitable for most networking applications, particularly in environments with low levels of electromagnetic interference.
STP vs UTP: Choosing the Right Cable
When it comes to deciding between STP and UTP cables, several factors should be considered, including the environment, required bandwidth, and potential sources of interference.
Use Cases for STP Cable
Industrial Environments: STP cables are commonly used in industrial settings where there is a high likelihood of interference from heavy machinery or other electrical equipment.
Outdoor Installations: If you’re installing a network in an outdoor environment where cables may be exposed to moisture, extreme temperatures, or other harsh conditions, STP cables provide an added layer of protection.
Use Cases for UTP Cable
Residential Networks: UTP cables are well-suited for residential networks, where interference levels are typically low and cost-effectiveness is a priority.
Office Environments: In office settings, UTP cables are often the go-to choice, offering a balance between affordability and performance.
STP |
UTP |
|---|
| Stands for Shielded twisted pair |
Stands for Unshielded twisted pair |
| This type of cables are shielded | This type of cables are unshielded |
| Installation of cable is difficult | Installation of cable is easy |
| Cables are heavier | Cables are less heavier |
| Cost is high | Cost is low |
| High data rates | Slow as compare to STP |
| Less noise and crosstalk | High noise and crosstalk |
 |  |
FAQs
What is STP (Shielded Twisted Pair)?
STP is a type of twisted pair cable that includes a shield around the wires to protect against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk. This shielding can be made of foil or braided metal.
What is UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)?
UTP is a type of twisted pair cable that does not have any shielding. It consists of pairs of copper wires twisted together to reduce interference and crosstalk but is more susceptible to external interference compared to STP.
What are the advantages of STP cables?
– Offers better protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI).
– Can be used in environments with high interference, such as industrial settings.
– Provides higher data transmission rates over longer distances compared to UTP.
What are the advantages of UTP cables?
– Less expensive and easier to install due to lack of shielding.
– Lighter and more flexible than STP cables.
– Sufficient for most residential or office networks with low EMI.
When should I use STP over UTP?
STP is preferred in environments with high electromagnetic interference, such as factories, industrial plants, or areas with heavy electrical equipment. It is also used in networks requiring high data rates or longer distances where protection from interference is essential.
When is UTP more suitable than STP?
UTP is typically used in home or office environments where electromagnetic interference is minimal. It is ideal for short-distance networking and applications with lower interference levels.
Which is more expensive, STP or UTP?
STP cables are generally more expensive than UTP cables because of the added shielding and more complex manufacturing process.
Which offers better performance, STP or UTP?
STP generally offers better performance in terms of resistance to interference, allowing for more reliable and stable network connections, especially in environments with high EMI. UTP, while cheaper and easier to install, may not perform as well in such conditions.
Conclusion
In the battle of STP vs UTP cables, there is no definitive winner. The choice between the two depends on various factors such as the level of electromagnetic interference, budget constraints, and the specific requirements of your network. By understanding the differences and advantages of each cable type, you can make an informed decision that ensures optimal network performance.
Remember, whether you opt for the shielding of STP cables or the cost-effectiveness of UTP cables, it’s crucial to use high-quality cables and ensure proper installation for the best results.
So, the next time you’re planning a network installation or upgrade, consider the unique characteristics of STP and UTP cables to make an informed decision and enjoy a robust and reliable network connection.


One thought on “STP Vs UTP”