Enterprise automation stands at a critical crossroads in 2026. While Robotic Process Automation has powered business efficiency for over a decade, a transformative technology is reshaping how organizations approach operational workflows. Agentic AI represents a fundamental shift from rule-based task execution to autonomous, goal-driven systems that reason, adapt, and make decisions independently. Whether you’re a student exploring automation technologies, a developer architecting intelligent systems, or an IT leader evaluating enterprise solutions, understanding the distinction between agentic AI and RPA is essential for navigating the future of work. This comprehensive guide examines both technologies through technical, operational, and strategic lenses to help you make informed automation decisions that drive real business value.
The Evolution of Enterprise Automation in 2026
Enterprise automation has progressed through distinct technological generations, each expanding what machines can accomplish with decreasing human intervention. The current inflection point between traditional Robotic Process Automation and emerging agentic AI systems represents more than incremental improvement. It marks a fundamental shift in how autonomous systems operate within business environments. The choice between Agentic AI vs RPA now determines whether organizations merely accelerate existing workflows or fundamentally reimagine how work gets done.
RPA: Rule-Based Process Automation
Definition
Robotic Process Automation is software technology that deploys configurable bots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks by mimicking human interactions with digital systems. RPA bots follow explicitly programmed workflows, executing sequences of actions across applications through UI automation or API integrations. These systems excel at handling structured data in predictable processes, operating like sophisticated macros that perform the same operations consistently without deviation. Unlike cognitive systems, RPA lacks understanding of context or purpose beyond its programmed instructions.
Advantages
- Proven reliability: Over a decade of enterprise deployment with mature platforms like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism
- Fast implementation: Can be deployed in days or weeks for well-defined processes, delivering immediate ROI
- Perfect accuracy: Executes tasks with near-100% consistency when inputs match expected formats
- Low technical barrier: Business users can build automations using visual, drag-and-drop interfaces without coding expertise
- Regulatory compliance: Fully auditable execution logs provide complete transparency for compliance requirements
Disadvantages
- Brittle architecture: Breaks when source applications change UI elements, requiring constant maintenance
- No adaptability: Cannot handle exceptions, variations, or scenarios outside programmed rules
- Limited intelligence: Processes structured data only, failing with unstructured documents, emails, or images
- Maintenance burden: Organizations report spending 30-40% of automation budgets on fixing broken bots
- Scalability challenges: Each new process variation requires separate bot development and testing
Common RPA Applications:
Invoice Processing: Extract data from standardized invoice formats and enter into ERP systems with perfect accuracy. Employee Onboarding: Create accounts, assign permissions, and enroll in benefits programs following predefined checklists. Furthermore, Report Generation: Pull data from multiple sources, format according to templates, and distribute on scheduled basis. Additionally, Claims Processing: Validate claim forms against rules, route to appropriate queues, and update status in tracking systems.
Agentic AI: Autonomous Intelligence Systems
Definition
Agentic AI represents intelligent systems capable of autonomous goal pursuit, decision-making, and adaptive behavior without step-by-step programming. Unlike rule-based automation, agentic systems leverage large language models, machine learning, and reasoning frameworks to understand objectives, plan multi-step actions, use tools and APIs, and adjust strategies based on outcomes and changing conditions. These systems perceive their environment through various data inputs, maintain context across interactions, and execute workflows that span multiple systems and require judgment calls. Therefore, agentic AI operates more like a digital colleague than a programmed script.
Advantages
- Autonomous decision-making: Analyzes situations, evaluates options, and takes action toward goals without constant human guidance
- Handles complexity: Processes unstructured data including documents, emails, images, and conversational inputs
- Adaptive learning: Improves performance over time through feedback and experience rather than requiring reprogramming
- Context awareness: Understands nuance, intent, and situational factors that influence optimal decisions
- Workflow ownership: Manages end-to-end processes across multiple systems, maintaining state and coordinating sequential steps
Disadvantages
- Higher complexity: Requires sophisticated infrastructure including vector databases, orchestration frameworks, and monitoring systems
- Less predictability: Autonomous decision-making introduces variability and potential for unexpected behaviors
- Governance challenges: Ensuring agents operate within acceptable boundaries requires new policy frameworks and oversight mechanisms
- Resource intensive: Demands significant compute power, specialized expertise, and ongoing model maintenance
- Maturity concerns: Deloitte reports only 14% of organizations have production-ready agentic solutions despite 30% actively exploring them
Emerging Agentic AI Applications:
Intelligent Underwriting: Analyzes diverse data sources including medical records, financial statements, and external databases to assess risk and recommend personalized insurance policies. Supply Chain Optimization: Monitors real-time conditions, predicts disruptions, and autonomously adjusts inventory levels and routing decisions. In addition, Customer Support Resolution: Understands customer intent from natural language, retrieves relevant context, and resolves complex inquiries across multiple interaction channels. Moreover, Financial Analysis: Gathers market intelligence, synthesizes earnings reports, identifies patterns, and generates investment recommendations aligned with client portfolios.
Technical Architecture Comparison
RPA System Components
- Bot designer with visual workflow builders for creating automation sequences
- UI automation engines for interacting with application interfaces through screen scraping
- API connectors and integration adapters for system-to-system communication
- Orchestrator platforms for scheduling, monitoring, and managing bot execution
- Credential vaults for secure storage of authentication information
- Fixed decision trees implementing if-then-else conditional logic
- Execution logs capturing every action for audit and debugging purposes
Agentic AI System Components
- Large language models providing natural language understanding and reasoning capabilities
- Orchestration frameworks coordinating multi-step workflows and tool usage
- Vector databases enabling semantic search and contextual memory retrieval
- Tool registries cataloging available APIs, functions, and system interfaces
- Planning modules breaking down complex goals into executable sub-tasks
- Perception layers processing multimodal inputs including text, images, and structured data
- Observability platforms monitoring agent behavior, performance, and policy compliance
Automation Execution Flow
RPA Execution Process
- Bot receives trigger event based on schedule or system condition
- Executes pre-programmed sequence of actions in exact order specified
- Interacts with applications through UI elements or API calls
- Processes data according to fixed transformation rules
- Evaluates conditions using deterministic boolean logic
- Logs every step and halts on any unexpected error or exception
- Requires human intervention to handle variations outside defined rules
Agentic AI Execution Process
- Agent receives goal or objective in natural language form
- Planning module decomposes goal into logical sub-tasks and strategies
- Agent selects appropriate tools and APIs from available registry
- Executes actions while maintaining context and state across steps
- Monitors outcomes and adapts approach based on intermediate results
- Handles exceptions by reasoning through alternative solutions
- Escalates to human oversight only when uncertainty exceeds defined thresholds
Real-World Applications and Strategic Fit
Ideal Scenarios for RPA
- Data migration: Moving records between systems with standardized field mappings and transformation rules
- Regulatory reporting: Generating compliance documents from database queries following fixed templates
- Order processing: Executing standard fulfillment workflows with predictable steps and structured inputs
- Scheduled backups: Automating routine system maintenance tasks that follow consistent procedures
- Account provisioning: Creating user accounts and assigning permissions based on role definitions
Where Agentic AI Excels
- Contract analysis: Reviewing legal documents to extract obligations, identify risks, and flag non-standard clauses
- Customer inquiries: Resolving complex support issues that require understanding context, sentiment, and previous interactions
- Fraud detection: Analyzing transaction patterns, identifying anomalies, and making risk-based decisions in real-time
- Research synthesis: Gathering information from diverse sources, evaluating credibility, and producing comprehensive summaries
- Dynamic pricing: Adjusting prices based on demand, competition, inventory levels, and market conditions
Industry-Specific Applications
| Industry | RPA Use Cases | Agentic AI Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Services | Account reconciliation, transaction processing, report generation | Credit risk assessment, investment recommendations, fraud analysis |
| Healthcare | Patient registration, insurance verification, appointment scheduling | Medical record analysis, treatment recommendations, diagnostic support |
| Manufacturing | Inventory updates, purchase order creation, shipping notifications | Predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, quality anomaly detection |
| Retail | Price updates, order confirmations, returns processing | Personalized recommendations, demand forecasting, customer sentiment analysis |
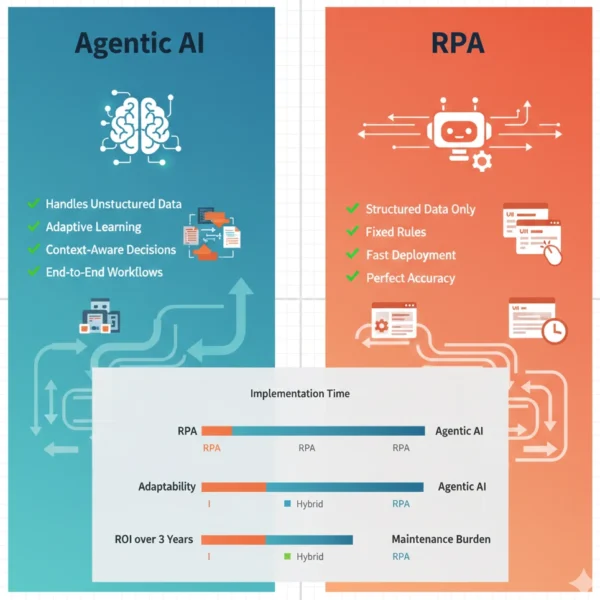
12 Critical Differences: Agentic AI vs RPA
Aspect | RPA (Robotic Process Automation) | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Model | Task-based execution following predefined scripts and workflows | Goal-oriented operation pursuing objectives through autonomous planning and adaptation |
| Decision Making | Deterministic logic using fixed if-then-else rules without interpretation | Contextual reasoning analyzing situations and selecting optimal actions dynamically |
| Data Handling | Structured data from databases, forms, and standardized documents only | Both structured and unstructured data including text, images, documents, and conversations |
| Adaptability | Rigid execution requiring manual reprogramming for any process variation | Dynamic adjustment learning from outcomes and adapting to changing conditions |
| Exception Handling | Fails or halts when encountering inputs outside programmed parameters | Reasons through unexpected scenarios attempting alternative approaches before escalation |
| Implementation Timeline | Days to weeks for well-defined processes with clear requirements | Months for complex deployments requiring data preparation and model training |
| Maintenance Requirements | High ongoing effort as 30-40% of budgets spent fixing bots broken by system changes | Lower maintenance as agents adapt to minor changes without manual intervention |
| Workflow Scope | Single-task or single-system automation with hand-offs between separate bots | End-to-end workflow ownership spanning multiple systems while maintaining context |
| Learning Capability | No learning mechanism, performs identically regardless of historical outcomes | Continuous improvement through reinforcement learning and feedback incorporation |
| Technology Foundation | UI automation, screen scraping, workflow engines, and API integrations | Large language models, machine learning, vector databases, and orchestration frameworks |
| Transparency | Complete auditability with step-by-step execution logs for compliance | Requires explainability frameworks as autonomous decisions may lack transparent reasoning |
| Maturity Level | Established technology with 10+ years of enterprise deployment and proven ROI | Emerging technology with only 14% of organizations having production-ready solutions |
Implementation Roadmap and Best Practices
Technology Selection Framework
- Process Assessment: First, analyze process complexity, data structure, exception frequency, and decision-making requirements to determine automation suitability.
- Data Evaluation: Then, assess whether inputs are structured and predictable or unstructured and variable, as this fundamentally constrains technology options.
- Business Value Analysis: Additionally, calculate potential time savings, error reduction, and cost benefits while considering implementation investment and timeline.
- Risk Tolerance: Furthermore, determine acceptable error rates, compliance requirements, and whether autonomous decision-making aligns with governance policies.
- Technical Readiness: Subsequently, evaluate existing infrastructure, team capabilities, and organizational change management capacity for successful deployment.
- Scalability Planning: Finally, consider long-term automation strategy, potential for reuse, and ability to expand scope as technologies mature.
Phased Deployment Approach
Phase 1: Foundation (Months 1-3)
- Map existing processes and identify automation candidates
- Establish governance framework and success metrics
- Build cross-functional team with business and technical stakeholders
- Select initial pilot targeting high-value, low-complexity workflow
Phase 2: Pilot (Months 4-6)
- Deploy RPA for stable, structured processes proving quick wins
- Launch agentic AI proof-of-concept on complex, judgment-heavy use case
- Measure performance against baseline and refine based on learnings
- Document integration patterns and operational procedures
Phase 3: Scale (Months 7-12)
- Expand successful pilots to additional processes and departments
- Develop hybrid workflows combining RPA execution with agentic decision-making
- Implement monitoring dashboards and continuous improvement cycles
- Build internal expertise through training and knowledge sharing
Implementation Best Practices
Success Factors
- Start with clearly defined, measurable business outcomes rather than technology exploration
- Involve process owners and end users early to ensure adoption and gather domain expertise
- Implement human-in-the-loop checkpoints for agentic AI decisions affecting customers or compliance
- Build observability from day one with logging, monitoring, and performance dashboards
- Establish guardrails limiting agent autonomy to acceptable risk boundaries
- Document decision logic and maintain version control for both RPA workflows and agent configurations
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Never automate broken processes, fix underlying issues before implementing RPA or agentic AI
- Avoid over-automation of tasks requiring genuine human judgment and empathy
- Don’t deploy agentic AI in production without extensive testing and validation frameworks
- Resist urge to automate everything, focus on high-value processes with clear ROI
- Never neglect change management and workforce preparation when introducing automation
- Don’t treat automation as one-time project, build sustainable operating model for continuous improvement
Cost, ROI and Performance Analysis
Initial Investment
RPA: $5,000-$50,000 per bot including platform licenses and development
Agentic AI: $100,000-$500,000 for infrastructure, models, and integration
Ongoing Costs
RPA: 25-35% of initial cost annually for maintenance and support
Agentic AI: 15-25% of initial cost plus compute and API usage fees
Time to Value
RPA: 2-8 weeks for typical process automation
Agentic AI: 3-6 months for production deployment
ROI Comparison: Three-Year Analysis
| Metric | RPA Deployment | Agentic AI Deployment | Hybrid Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 Net Benefit | $150,000 | -$50,000 | $100,000 |
| Year 2 Net Benefit | $180,000 | $200,000 | $350,000 |
| Year 3 Net Benefit | $160,000 | $400,000 | $550,000 |
| 3-Year Total ROI | 490% | 620% | 780% |
| Maintenance Burden | High and increasing | Moderate and stable | Moderate overall |
The hybrid approach combining RPA for structured tasks with agentic AI for complex workflows delivers superior three-year ROI compared to either technology alone. RPA provides immediate value but faces scaling challenges as maintenance costs accumulate. Agentic AI requires higher upfront investment but delivers accelerating returns as agents handle increasingly sophisticated scenarios. Organizations achieving best results deploy both strategically, using each technology where it provides maximum advantage.
Performance Characteristics
RPA Performance Profile
- Processing Speed: 3-5x faster than human execution for repetitive tasks
- Accuracy Rate: 99.9%+ when inputs match expected formats exactly
- Scalability: Linear scaling requiring additional bots for increased volume
- Availability: 24/7 operation with minimal downtime for maintenance
- Failure Rate: 15-25% of bots break monthly due to application changes
Agentic AI Performance Profile
- Processing Speed: Variable depending on reasoning complexity and API calls
- Accuracy Rate: 85-95% for complex tasks requiring judgment and interpretation
- Scalability: Single agent handles diverse scenarios without separate configurations
- Availability: Continuous operation with graceful degradation capabilities
- Adaptation Rate: Self-adjusts to process changes reducing maintenance interventions
Hybrid Automation Strategy: Best of Both Worlds
Strategic Integration Framework
The most successful enterprise automation strategies in 2026 combine RPA and agentic AI rather than choosing between them. This hybrid approach deploys RPA for high-volume, structured execution while leveraging agentic AI for complex decision-making, unstructured data processing, and exception handling. Consequently, organizations achieve both operational efficiency and intelligent adaptability.
Hybrid Architecture Patterns
Pattern 1: Hierarchical Orchestration
Agentic AI operates as the orchestration layer making high-level decisions about workflow routing, while RPA bots execute specific tasks:
- Agent analyzes incoming customer request and determines optimal handling path
- Agent invokes appropriate RPA bot to execute standardized processing steps
- Bot completes structured tasks and returns results to agent
- Agent synthesizes outputs and makes final decisions or recommendations
- Example: Insurance claims processing where agent assesses claim complexity and routes simple cases to RPA while handling complex scenarios autonomously
Pattern 2: Exception Escalation
RPA handles standard workflows until encountering exceptions that trigger agentic AI intervention:
- RPA processes transactions following established rules and patterns
- When bot encounters unexpected input or edge case, escalates to agent
- Agent analyzes exception using contextual reasoning and decides resolution
- Agent either resolves directly or provides guidance for RPA to continue
- Example: Invoice processing where RPA handles standard formats but agent interprets non-standard documents and extracts relevant information
Real-World Hybrid Implementation
Case Study: Enterprise Customer Onboarding
Challenge: Financial services company needed to onboard 10,000+ business customers annually with highly variable documentation and complex compliance requirements.
Hybrid Solution:
- Agentic AI Initial Assessment: Agent analyzes submitted documentation bundle, extracts key information from unstructured documents, and assesses completeness and compliance risk level.
- RPA Data Entry: For standard customer data, RPA bot populates CRM system, creates accounts across multiple platforms, and generates welcome materials.
- Agentic AI Risk Evaluation: Agent performs comprehensive background checks, analyzes financial statements, and makes preliminary risk classification with confidence scores.
- RPA Workflow Routing: Based on agent’s risk assessment, bot routes to appropriate approval queue and triggers relevant compliance checks.
- Human-in-the-Loop: High-risk cases or low-confidence agent decisions escalate to human reviewers with full context and supporting analysis.
Results: 60% reduction in processing time, 40% decrease in manual review requirements, 95% accuracy for automated decisions, and significant improvement in customer experience through faster onboarding.
Integration Considerations
Technical Integration Points
- Shared data repositories enabling seamless information exchange between agents and bots
- API gateways providing unified interface for both RPA and agentic AI tool access
- Event-driven architecture supporting asynchronous communication and workflow coordination
- Common observability platform monitoring performance across hybrid automation landscape
- Unified governance framework ensuring consistent policy enforcement regardless of automation type
Organizational Integration
- Cross-functional automation center of excellence managing both RPA and agentic AI initiatives
- Standardized assessment criteria determining which technology fits specific use cases
- Shared development practices and reusable components across automation technologies
- Integrated training programs building capability in both traditional and agentic automation
- Unified success metrics measuring overall automation value rather than individual technologies
Frequently Asked Questions: Agentic AI vs RPA
Making Strategic Automation Decisions in 2026
The decision between Agentic AI vs RPA is not binary but strategic, requiring careful analysis of process characteristics, organizational capabilities, and business objectives. Both technologies deliver transformative value when deployed appropriately, and their combination creates automation capabilities exceeding either approach alone.
Deploy RPA When:
- Processes are highly standardized with minimal variation
- Data inputs are structured and follow consistent formats
- Quick wins and immediate ROI are priorities
- Complete audit trails and deterministic outcomes are required
- Team lacks advanced AI expertise or infrastructure
- Transaction volumes are high but complexity is low
Deploy Agentic AI When:
- Workflows require contextual judgment and decision-making
- Inputs are unstructured including documents, emails, or conversations
- Processes involve significant exceptions and edge cases
- End-to-end workflow ownership spanning systems is needed
- Adaptability to changing conditions provides competitive advantage
- Human expertise is scarce or difficult to scale
Strategic Recommendation for 2026:
Begin automation journey with targeted RPA deployments that deliver immediate value while building organizational confidence and establishing governance foundations. Simultaneously, pilot agentic AI on one complex, high-value use case where intelligent decision-making creates differentiated capabilities. This parallel approach generates quick wins validating automation investment while developing expertise in emerging agentic technologies. As capabilities mature, transition toward hybrid architectures where RPA handles structured execution and agentic AI provides intelligent orchestration, exception handling, and adaptive optimization. Organizations pursuing this balanced strategy position themselves to capture both immediate efficiency gains and long-term competitive advantages from autonomous intelligence.
The automation landscape in 2026 rewards organizations that understand these technologies as complementary capabilities rather than competing alternatives. Whether you’re a student learning automation fundamentals, a developer building intelligent systems, or an enterprise leader making strategic technology investments, recognizing when to apply rule-based execution versus autonomous reasoning determines your success in the AI-powered future of work. Your competitive advantage comes not from choosing sides in the agentic AI versus RPA debate, but from mastering both and deploying each where it creates maximum business value.
Related Topics Worth Exploring
Intelligent Process Automation
Discover how IPA combines RPA, AI, and workflow orchestration to create comprehensive enterprise automation solutions.
Large Language Models in Enterprise
Learn how foundation models power agentic AI systems and transform knowledge work across industries.
Automation Governance Frameworks
Explore best practices for managing autonomous systems, ensuring compliance, and maintaining human oversight.